Scoping Guidance Tool Overview
1. Project Summary
Summary of proposed work
2. Project Activities
Definitions of Activities
Detail the individual activities involved (e.g. capital dredging using suction dredger; ongoing maintenance dredging).
3. Environmental Change
Identify environmental changes (qualitative & quantitative).
4. N2K Features
Identify designated sites & N2K features that are or could be present (e.g. subtidal sandbanks; mudflats; seals).
5. Feature Sensitivity
Identify the N2K features that are sensitive to the activity & it’s likely environmental change.
6. Risk Assessment
Determine whether features are going to be exposed to an environmental change to which they are sensitive. Answer questions such as:-
- Is there a pathway?
- What is the magnitude of the change?
- What is the sensitivity of the feature receptor?
7. Screen-out Features
Identify those features which will not be exposed to environmental change or are not sensitive to any of the changes.
8. Features to Assess
Identify those features that need to be considered in an AA because they are sensitive to,& exposed to, an environmental change.
9. Assessment methods
Identify the impact assessment methods that are most appropriate.
Print Summary
- Summary print page whihc includes information on:
- Summary of project
- Activities selected
- Features selected
- Environmental Changes (Identified by both activities and features)
- Environmental Change & Feature Matrix
- Methods (Common to environmental changes derived from both activities and features)
View Impacts Tree
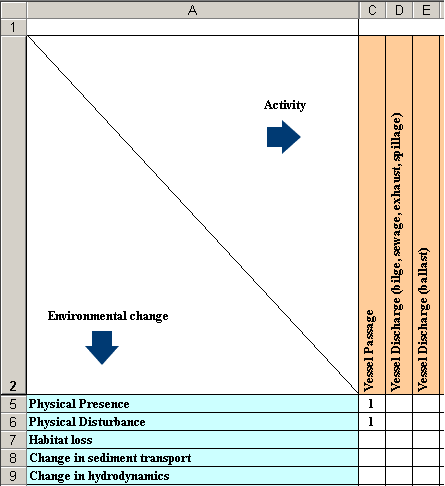
Port activities linked to environmental change
Environmental changes related to features
The Impacts Tree is a dynamically expandable/collapsible tree created from the proposal/activities and features selected by the user. The tree attempts to demonstrate the complexity of the potential pathways between activities and features. At the environmental change level (beneath activities), there is also a link to allow the user to go straight to a list of methods for any given environmental change.
View Methods
Port activities linked to environmental change
Environmental changes related to features
The user is asked to select an environmental change from an automatically retrieved drop-down menu defined from previous proposal/activity/N2K feature choices. The user's selection is then submitted and a query is made to the database to return a list of appropriate methods.
List of Methods
The list produced includes all methods from the list that are appropriate, but it does not consider the appropriateness of the methods – e.g. is a full computer model required to assess the impact of moving a mooring? As such, it is not easy to differentiate between a method that is costly, time consuming and that requires a detailed amount of data (for example a detailed mathematical model, as might be required for a large scale development) or a method that can be based on more generic data over a shorter period of time (such as the application of expert judgment for a small scale development)
Printable Summary
As the user goes through the tool, the selections made are stored in cookies and a printer friendly summary of what has been chosen can be found here.
Details that are included (depending on what has been selected by the user) :
- Date & Time (UK)
- Proposal selected
- Activities selected
- N2K Features selected
- Environmental Changes Identified (NB this requires proposal, activities and features to have been selected)
Port activities linked to environmental change
It is important to note that the activities listed have the potential to lead to the associated changes only. The actual changes that result may include some or all of the potential changes, with both the changes that occur and the significance of those changes being site specific. As such, the lists of potential changes should be viewed as a worst case scenario.
Definitions of Activities
Definitions
of Environmental Change
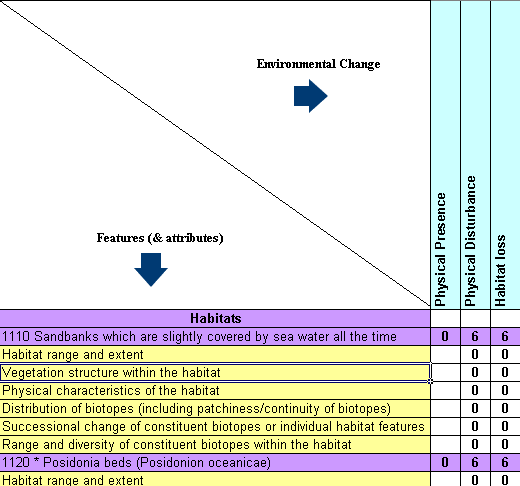
Environmental changes related to features (and associated attributes)
It should be noted that the identification of changes with the potential to affect the features listed is made on a worst-case basis – i.e. if it is considered that there is potential for that change to affect that feature the link is highlighted. Such an assumption will need to be tested on a site by site basis, as the potential for impact is not purely related to the type of change and the particular receptor, but also to issues such as whether the change is large enough to exceed the tolerance of the receptor.
Definitions of Environmental Change
Definitions of Features
Definitions of Features
